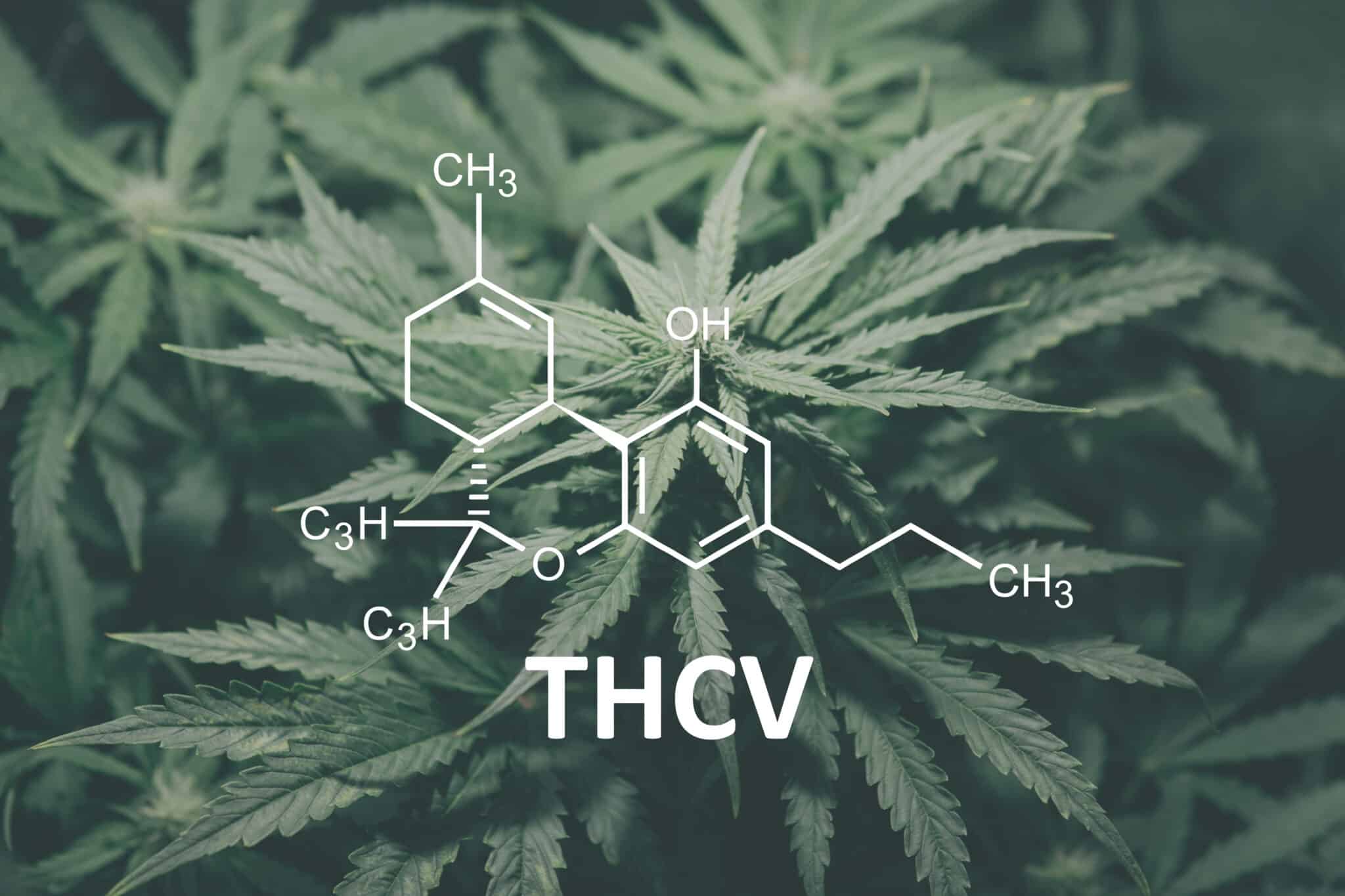
THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) are both cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant, but they have distinct differences in their molecular structure and ≠≠
What is THCV?
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a cannabinoid found in the cannabis sativa plant. Unlike its more famous counterpart, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), THCV doesn’t seem to significantly affect thinking or produce the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis use – potentially helping highly sensitive cannabis users to avoid “greening out.”
This compound has garnered attention for its unique properties, leading some to refer to it as “diet weed” due to its purported appetite-curbing effects.
THCV is most prevalently found in Sativa strains of cannabis and is known for producing a motivated, alert, and energized feeling in users. This sets it apart from the typically relaxing effects associated with THC. At the molecular level, THCV is a propyl analogue of THC, meaning it shares a similar structure but with some variations that significantly alter its effects on the body.
One of the key differences in their action relates to their interaction with the body’s cannabinoid receptors. THCV acts as a cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) antagonist at lower doses, blocking the receptor’s activity. At higher doses, it can act as a CB1 receptor agonist and also as a partial agonist for the cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2)
Is THCV Safe to Try?
As always, at Cannabis Doctor X, we recommend you talk with a medical doctor before trying substances like THC. In research contexts, such as randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies, THCV, alongside CBD, has been evaluated for safety and efficacy, underscoring the importance of controlled conditions to ascertain its effects and potential health benefits.
In terms of specific applications, studies have also looked into THCV’s impact on lipid and glucose metabolism, hinting at its potential for treating conditions such as diabetes, with research aiming to clarify its efficacy and safety in these contexts
The Difference Between THCV vs THC
Molecular Structure
At a molecular level, THCV and THC are similar, with THCV being an analog of THC. The main structural difference is that THCV has a slightly shorter hydrocarbon chain compared to THC. This difference in structure means that while they may share some properties, their effects on the body can vary significantly.
THCV and Appetite:
One of the most notable differences between THCV and THC is their effect on appetite. While THC is known to stimulate appetite, making users feel “the munchies,” THCV is believed to have the opposite effect, potentially suppressing appetite. This property of THCV makes it a subject of interest for weight management and obesity research.
Psychoactivity
THC is well-known for its psychoactive effects, which is the feeling of being “high” that is commonly associated with cannabis use. THCV, on the other hand, behaves differently depending on the dose.
At lower doses, THCV does not produce psychoactive effects, and it might even act to counteract some of the psychoactive effects of THC. However, at higher doses, THCV may exhibit psychoactive properties, though the experience may differ from that of THC.
Interaction with Endocannabinoid System
Both THCV and THC interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating various physiological processes. However, they do so in different ways. THC activates and boosts the CB1 receptor, contributing to its psychoactive effects.
THCV, however, acts as an antagonist of the CB1 and CB2 receptors at low doses, which means it can block or reduce the activity of these receptors. At higher doses, THCV can become an agonist of these receptors, though its effects are still being studied.
Benefits of THCV
Due to its unique properties, THCV is being researched for its potential therapeutic benefits, including appetite suppression, regulation of blood sugar levels, and reduction of anxiety, without the psychoactive effects associated with THC. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential health benefits and applications of THCV.
Research has suggested that THCV may offer several benefits, including increases in energy and motivation without the “munchies” effect commonly associated with THC consumption. A study mentioned by Marijuana Moment noted that both THC-only and THCV gummies increased activity, exercise performance, motivation, and well-being compared to a placebo, highlighting THCV’s potential for enhancing physical activity and mental state without promoting hunger
Is THCV Psychoactive?
THCV exhibits a complex relationship with psychoactivity, which is distinctly dose-dependent. At lower doses, THCV appears to act in a manner similar to CBD (cannabidiol), moderating and reducing some of the traditional psychoactive effects associated with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis.
This modulation occurs because THCV can act as an antagonist at CB1 receptors, the primary receptor type through which THC exerts its psychoactive effects. In this capacity, THCV does not produce the “high” typically associated with cannabis use and may even dampen the psychoactive effects of THC
Cannabis Doctor X is Here For You
While THCV and THC share a similar molecular structure, their differences in the length of their hydrocarbon chains lead to varied effects on the body, making THCV a cannabinoid of interest for its unique properties and potential health benefits. If you are considering obtaining a medical marijuana card in Florida, feel free to give us a call!
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7819335/
https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/39/10/1777/129/Efficacy-and-Safety-of-Cannabidiol-and